Archives

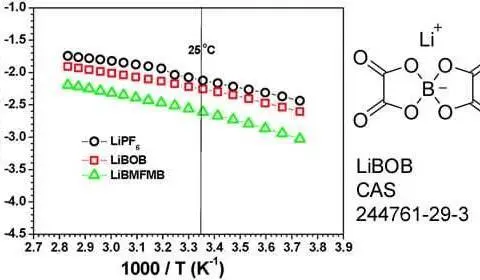
LiBOB
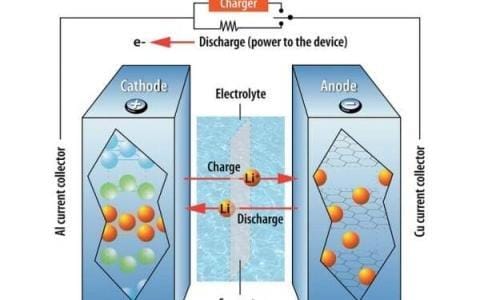
Application LiBOB is a novel boron based Li salt electrolyte material for Li ion batteries. It is environmentally friendly with good film forming property and high thermal stability and is compatible with a variety of anodes and metal oxide cathode. Synonyms Lithium Bis(oxalato) Borate; Borate(1-), bis[ethanedioato(2-)-κO1,κO2]-, lithium (1:1) [ACD/Index Name];Lithium bis[ethanedioato(2-)-κ2O1,O2]borate(1-); Lithium 2,3,7,8-tetraoxo-1,4,6,9-tetraoxa-5-boraspiro[4.4]nonan-5-uide; Lithium bis(oxalate)borate;

LiODFB
Application LiODFB (Lithium oxalyldifluoroborate) is first reported as the salt for improved electrolyte of Li-ion battery. This salt was found to have the combined advantages of lithium bis(oxalato)borate (LiBOB) and LiBF4 due to its chemical structure comprising the half molecular moieties of LiBOB and LiBF4. Compared with LiBOB, the salt is more soluble in linear
LiBF4
Application LiBF4 (Lithium tetrafluoroborate) has been extensively tested for use in commercial secondary batteries, an application that exploits its high solubility in nonpolar solvents. Although BF4− has high ionic mobility, solutions of its Li+ salt are less conductive than other less associated salts. As an electrolyte in Lithium-ion batteries, LiBF4 offers some advantages relative to
Copyright © FCAD (1996-2024). All Rights Reserved. FCAD, the FCAD logo and all other FCAD marks contained herein are trademarks of FCAD Intellectual Property and/or FCAD affiliated companies. Privacy Statement | Terms of Use | Copyright © 1996-2024
